Search & filter
Search & filter helps users find a single or set of records.
Overview
Search & filter can help users locate a specific record or create a set of related records. In general, filters are applied after a search, to further refine a broader search set.
The search process is comprised of five steps: 1. Initiate, 2. Show results, 3. Refine, 4. View details, 5. Return to results.
Steps
1. Initiate search
Design principle
Help users understand what they can find.
Components to use
| Component | Intent | Tradeoff |
|---|---|---|
| App bar search | Use for searching the full app. | Broad scope. |
| Local search | Use for searching with in a page or section. | Limited scope |
| Category search | Communicates what can be searched. | More decisions about category to use. |
| Advanced search | Finding a specific record. Communicates what can be searched. | More decisions about which field to use. |
Advanced search and filtering should NOT be used together. An advanced search allows users to locate a specific, known result. Search + filter allows users to start with a broad search query and iteratively filter down their filter set, using the results themselves to better understand the domain.
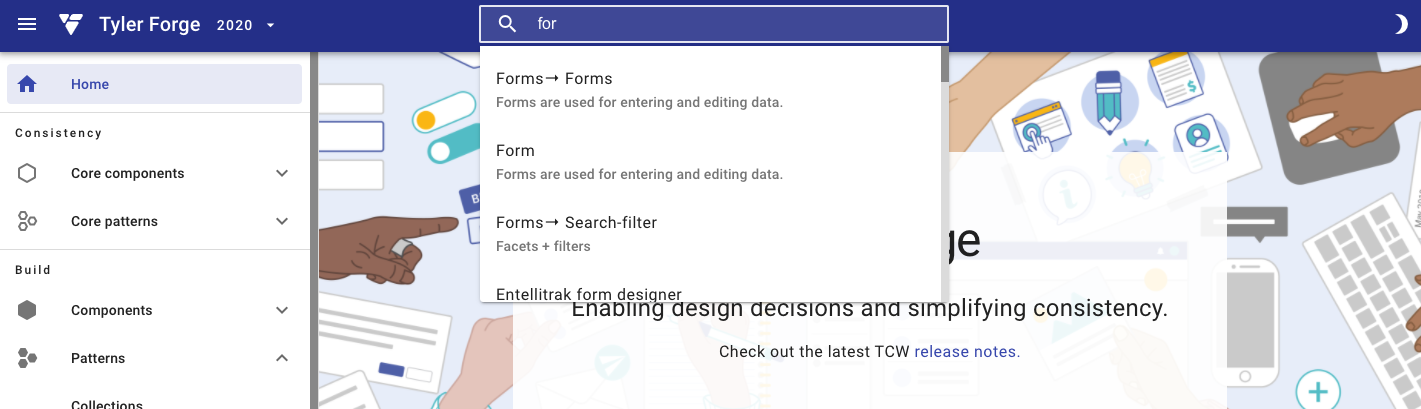
The Forge site uses an app bar search to allow users to search the full site.
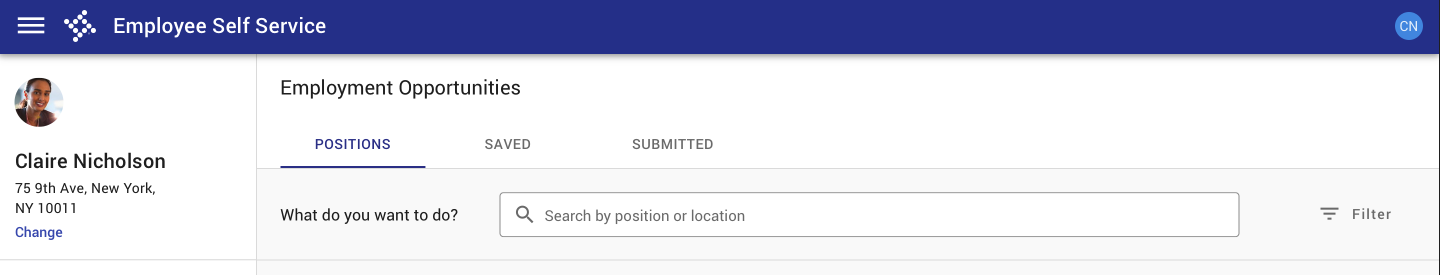
A local search allows users to search a page or section.
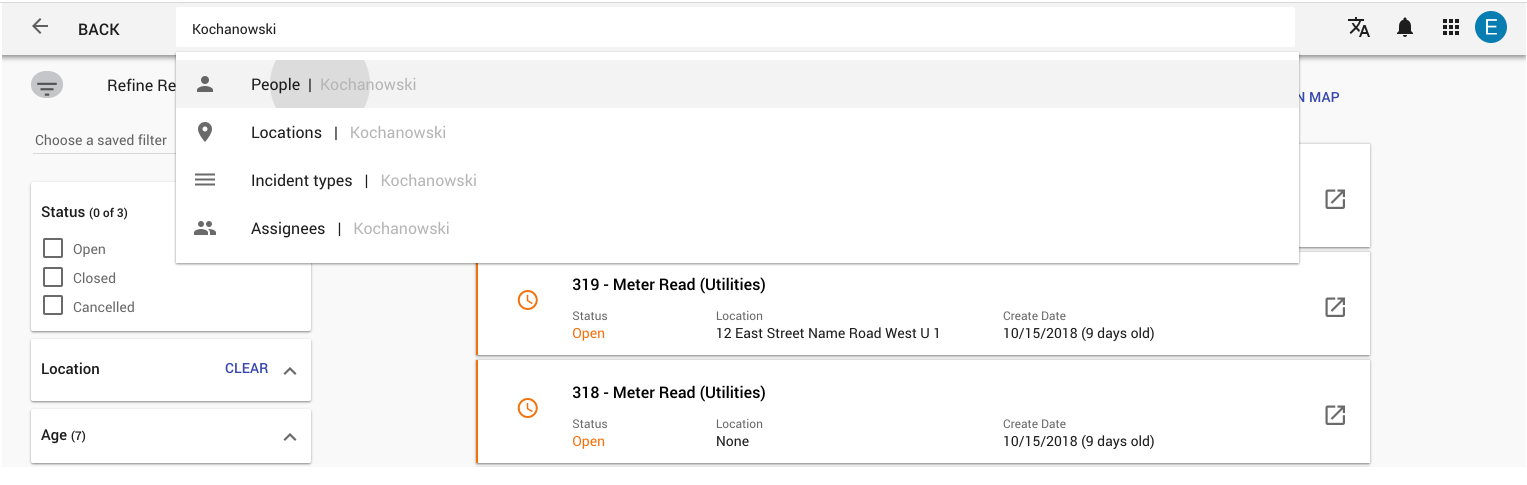
A category search allows users to search within specific categories, but requires additional decisions around which category to pick.
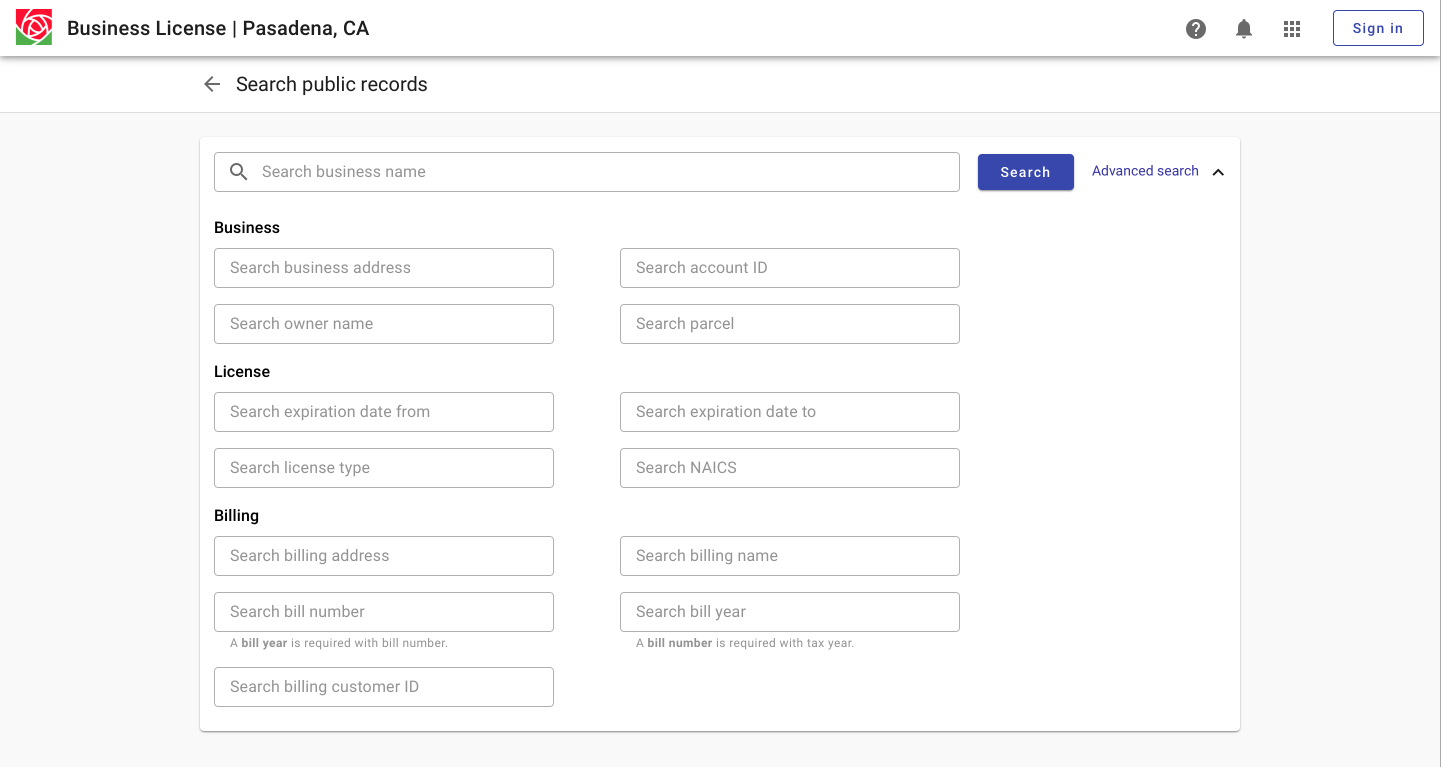
An advanced or multi field search communicates what can be searched but results in more decisions around which field to use.
2. Show results
Design principle
Use structure (result ordering, information design, and visual hierarchy) to help users match results with mental model.
Components to use
| Component | Intent | Tradeoff |
|---|---|---|
| Task cards | Better for displaying a few label value pairs per record. Better for expansions. | Can view fewer total results on a page, not optimized for mobile. |
| Cards | Better for visual or nonhomogenous data. | Not optimized for large blocks of text. |
| List | Better for scanning, can view more results on a page. | Not optimized for image heavy data. |
See also Collections guidance.
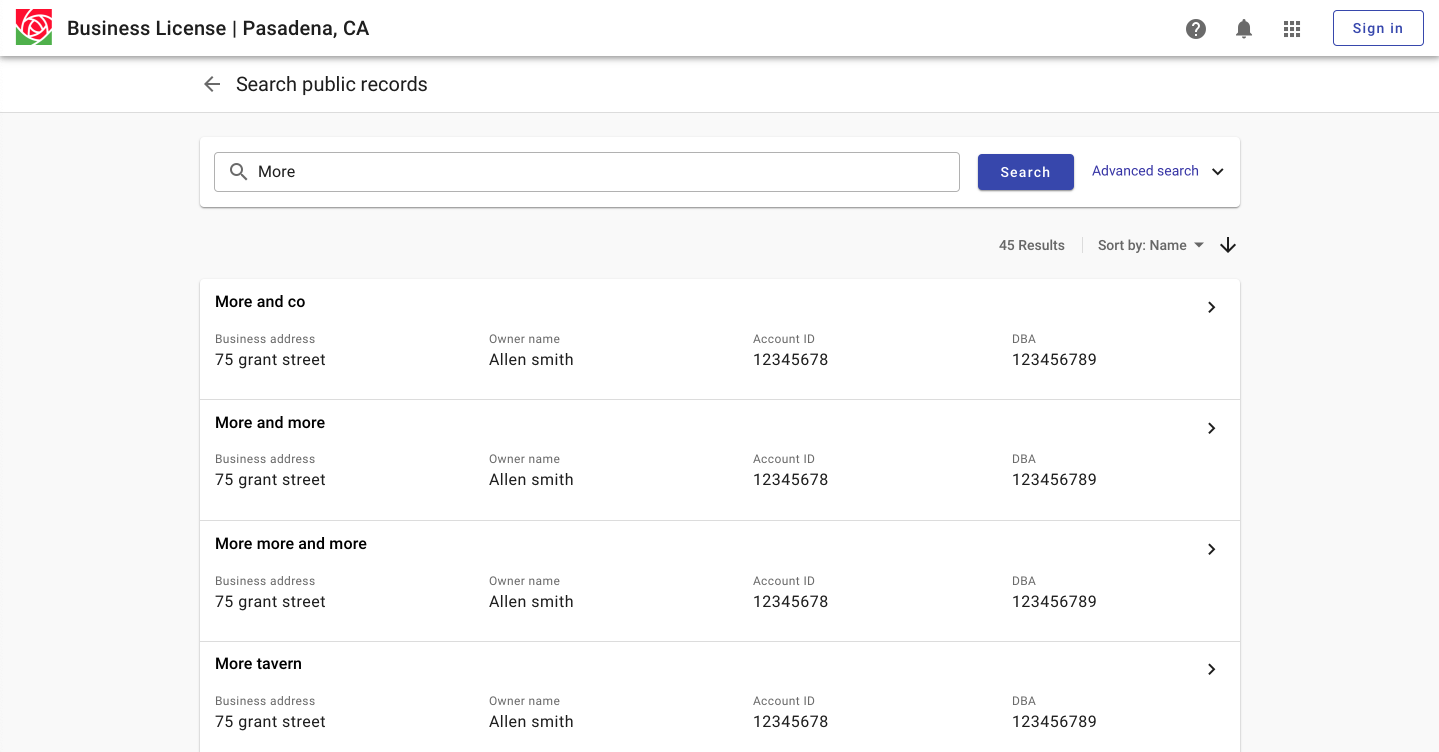
Displaying results as task cards can facilitate displaying summary information.
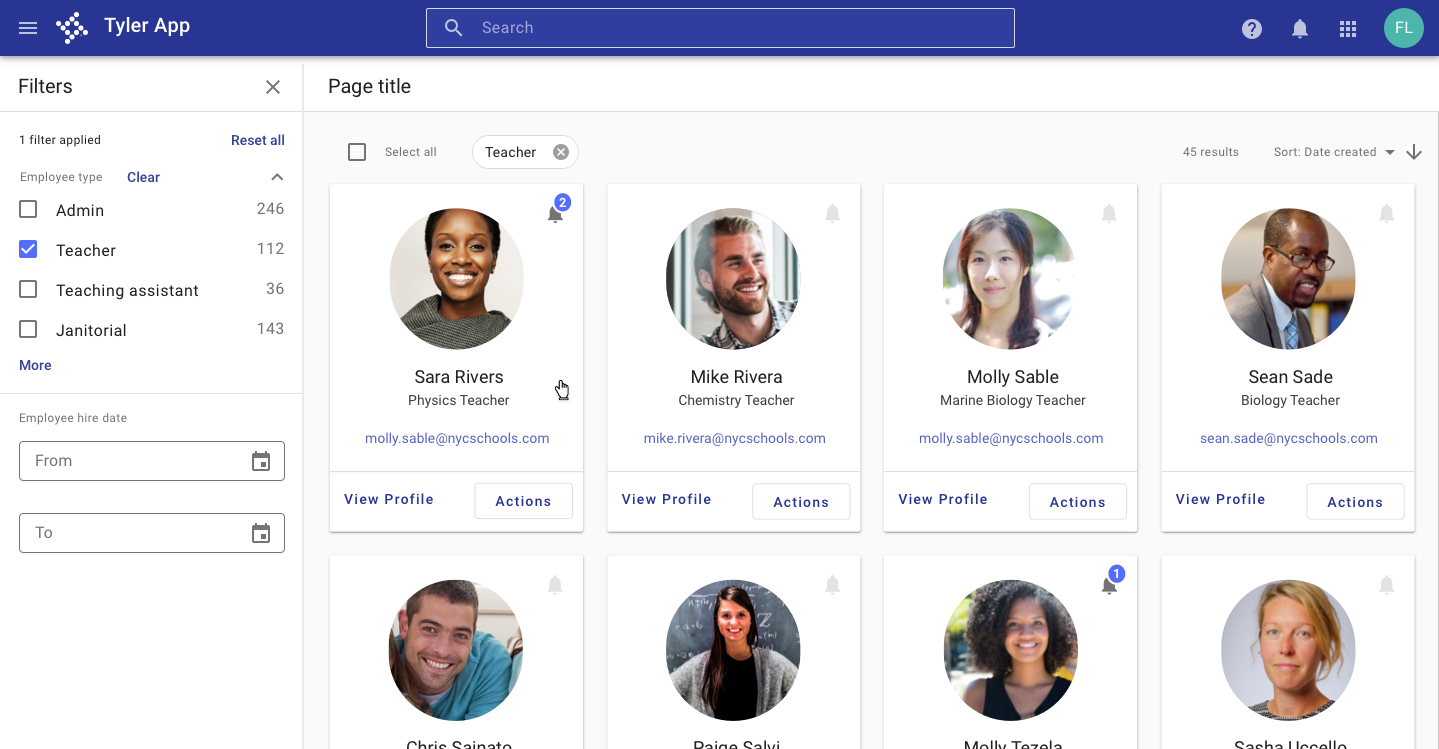
Displaying results as cards is better for visual data.
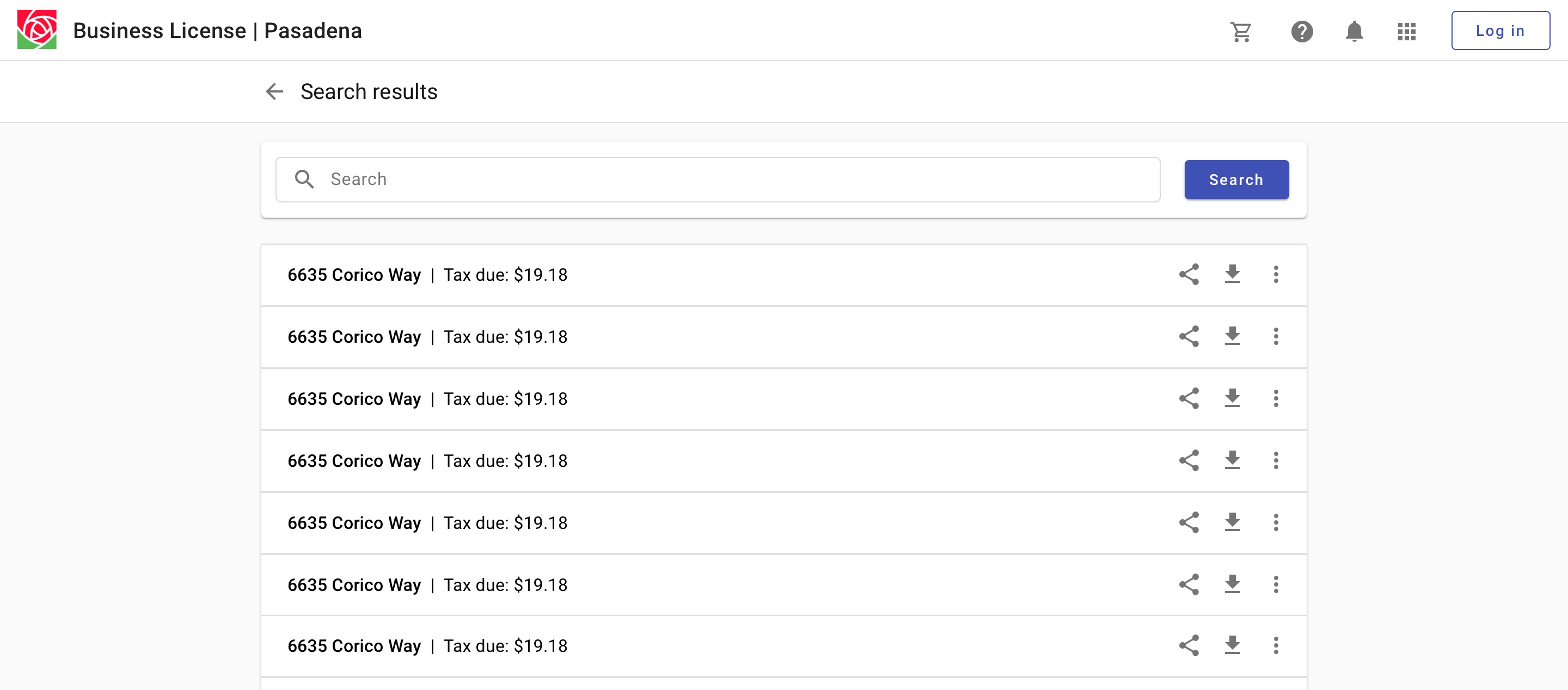
Displaying results as a list facilitates scanning.
3. Refine results
Design principles
- Help users iteratively refine selections by providing logical filter categories.
- Indicate which filters have been applied, especially if the filter sheet has been closed.
Components to use
See Filter sidesheet
| Component | Intent | Tradeoff |
|---|---|---|
| Sidesheet with scrim | Better when screen real estate is limited. Filters should be applied with an explicit "Apply" option. | Loss of context / detail for records. |
| Persistent sidesheet | Allows users to reference filters and search results at the same time. | Not optimized for smaller screen sizes. |
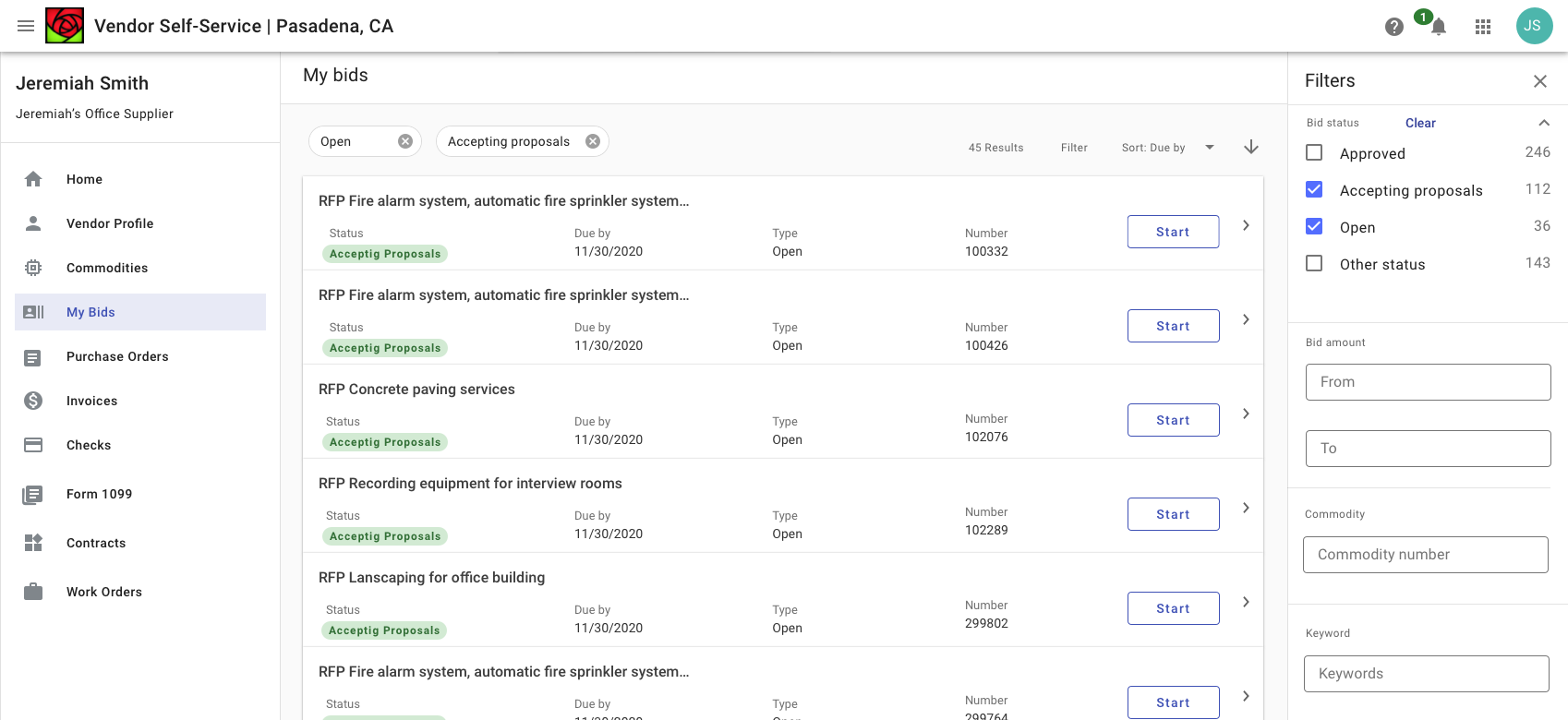
A persistent filter side sheet allows users to reference filters and search results at the same time and is better optimized for desktop. With a lefthand navigation, filters are shown to the right. With no navigation, filters are displayed on the left by default.
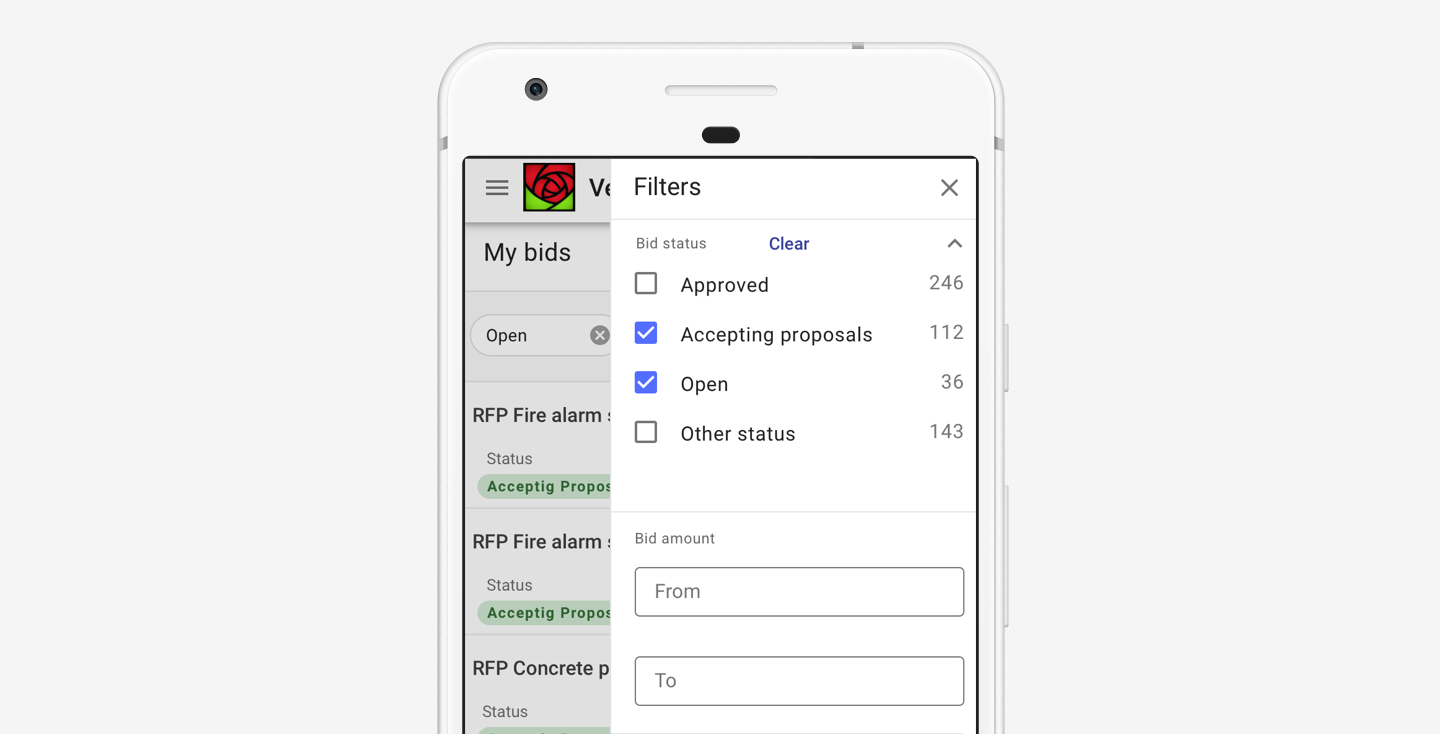
A sidesheet with scrim is better for mobile contexts.
4. View detail
Design principles
- Progressive disclosure.
- Match content amount to mode (expansions and dialogs for less detail; full page for more detail).
Components to use
| Component | Intent | Tradeoff |
|---|---|---|
| Expansion / sidesheet | View detail in context - lower interaction cost. | Not as much space for detail. |
| Dialog | Focused experience, may facilitate editing. | Loss of context. |
| Detail page | Focused experience, better for displaying more information. | Loss of context. |
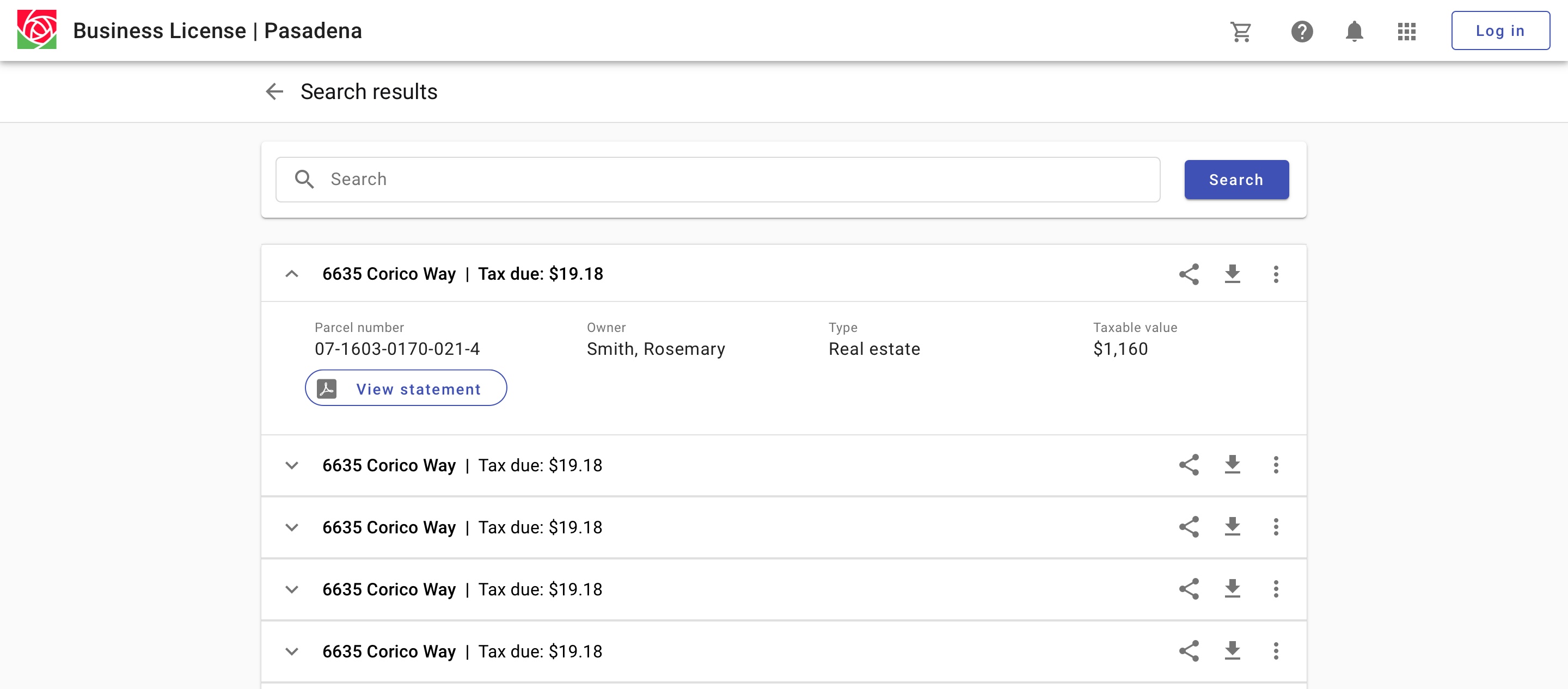
Search results with expansions allow for displaying content in context.
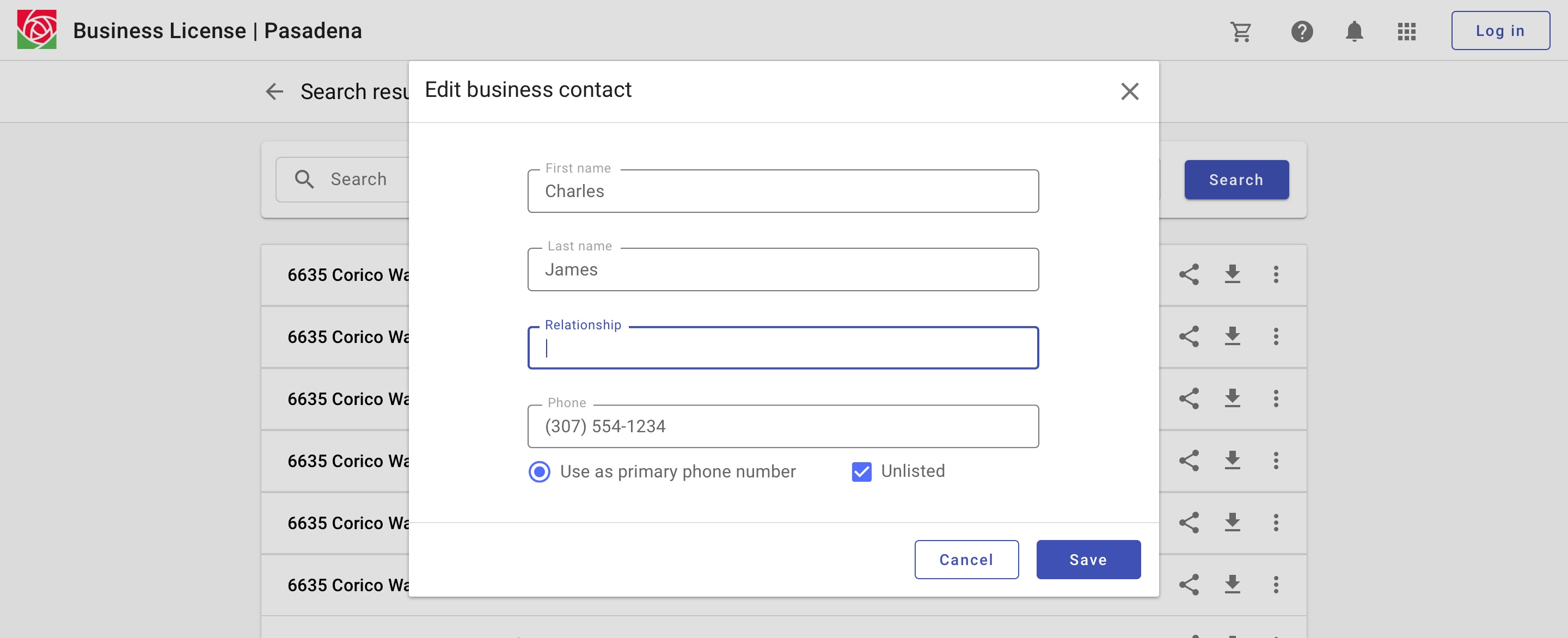
Displaying detail in a dialog allows for a focused experience and may facilitate editing.
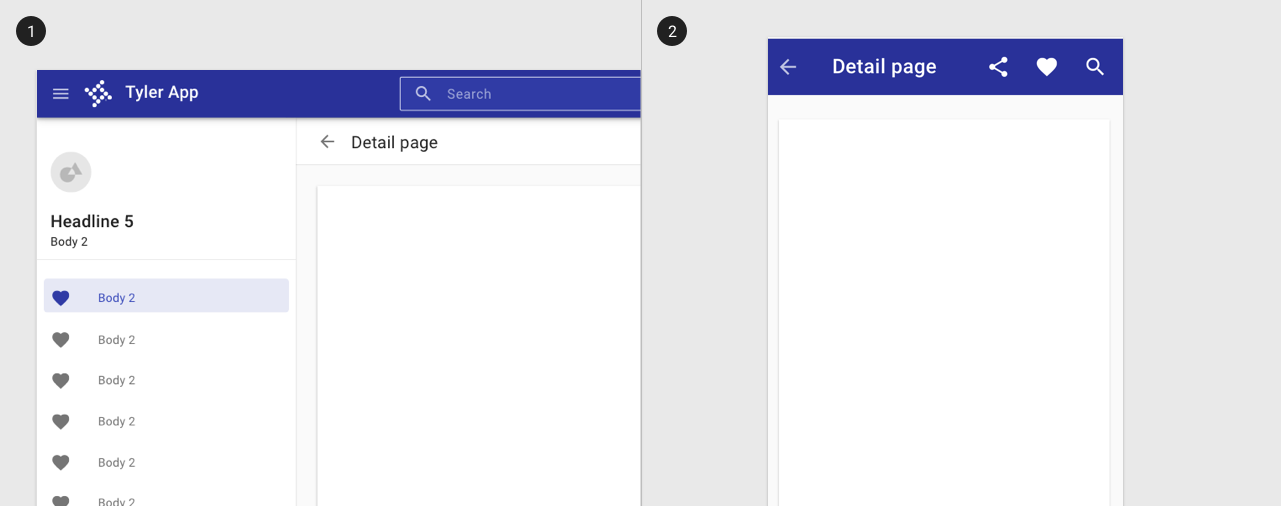
Displaying detail in a separate page better facilitates more information. Use a back arrow to allow users to navigate back to a search.
5. Return to results
Design principle
Return users to their prior screen position and state, such as their vertical scroll position, to facilitate recall and task resuming.
Components to use
Toolbar with back arrow.

Displaying detail in a separate page better facilitates more information. Use a back arrow to allow users to navigate back to a search.
Related
Search is composed of the following components:
Forms are related to the following patterns: